5TH Grade Science [Science 5] |
|
|--Characteristics living things
|--Reproduction and change
|--Adaptations
|--Ecology
|--Matter
|--Motion
|--Energy
|--Electricity
|--The changing earth
|--The earth's resources
|--Climate
|--Astronomy
|--Skeletal and Muscular System
|--Digestive System
|--Circulatory System
|--Nervous System
Required Textbook: A Beka SCIENCE 5, Pensacola, Florida, current edition.
[a] Simple Machines/Technology
[i] Distinguish between natural objects and objects made by humans. Objects can be categorized into two groups, natural and designed.
[ii] Tools help scientists make better observations, measurements, and equipment for investigations. They help scientists see, measure, and do things that they could not otherwise see, measure and do.
[iii] Machines can be used to alter a force. Functioning of machines is affected by friction.
[b] Light, heat, electricity, and magnetism
[i] Light travels in a straight line unless it strikes an object Light can be reflected by a mirror, refracted by a lens, or absorbed by the object.
[ii] Heat can be produced in many ways such as burning, rubbing, and mixing chemicals. The heat can move from one object to another by conduction.
[iii] The path of light may be affected by lenses. These can have concave or convex surfaces.
[c] Properties of objects and materials
[i] Objects have many observable properties, including size, weight, shape, color, temperature, and the ability to react with other substances. These properties can be measured using tools such as rulers, balances, and thermometers.
[ii] Objects are made of one or more materials, such as paper, wood, and metal. Objects can be described by the properties of the materials from which they are made, and these properties can be used to separate or sort a group of objects or materials.
[iii] Materials have different states - solid, liquid, and gas. Some common materials such as water can be changed from one state to another by heating or cooling.
[iv] The properties of matter can be identified and measured (mass and weight).
[d] The characteristics of organisms
[i] Plants require air, water and light.
[ii] Each plant or animal has different structures which serve different functions in growth, survival, and reproduction.
[iii] Plants and animals have life cycles that include being born, developing into adults, reproducing, and eventually dying.
[iv] Plants and animals closely resemble their parents. Many characteristics of an organism are inherited from the parents of the organism, but other characteristics result from, an individual's interactions with the environment.
[v] All animals depend on plants. Some animals eat plants for food. Other animals eat animals that eat the plants.
[vi] Plants have complex structures with specialized functions.
[vii] Understand the characteristics of seed bearing and non-seed bearing plants, how green plants differ from non-green plants.
[viii] Understand the oxygen-carbon dioxide cycle.
[e] Personal health
[i] Different substances can damage the body and how it functions. Such substances include tobacco, alcohol, over-the-counter medicines, and illicit drugs. Some substances such as prescription drugs can be beneficial but any substance can be harmful.
[ii] Humans have specialized systems responsible for body functioning. Understand the parts and functions of the body.
[iii] There are diseases associated with each system of the body. Understand diseases associated with the body systems.
[iv] There are diseases associated with drug abuse. Understand the effects of drug abuse on the body.
[f] Types of resources
[i] Resources include those things that we get from the living and nonliving environment to meet the needs and wants of a population.
[ii] Some resources include basic materials, such as air, water, and soil; some are produced from basic resources, such as food, fuel, and building materials; and some resources are nonmaterial, such as quiet places, beauty, security, and safety.
[iii] The supply of many resources is limited. If used, those materials can be extended through recycling and decreased use.
[iv] Energy consumption impacts the environment. Alternative energy forms have been developed to conserve natural resources.
[v] Understand the relationship between energy and the environment. As well as the kinds, uses and problems associated with renewable and non-renewable resources.
[g] Water and Oceanography
[i] The topography of the ocean floor is in constant change. Understand the structure and constant changing of the ocean floor.
[ii] Understand the changes which occur in the oceans and their effect on the earth. Understand relationships among oceans, weather, and climate.
[iii] Water, which covers the majority of the Earth's surface, circulates through the crust, oceans, and atmosphere in what is known as the water cycle.
[iv] Water is a solvent. As it passes through the water cycle it dissolves mineral sand gases and carries them to the oceans.
[v] The atmosphere is a mixture of oxygen, nitrogen, and trace gases that include water vapor The atmosphere has different properties at different elevations.
[vi] Clouds, formed by the condensation of water vapor, affect weather and climate. Some do so by reflecting much of the sunlight that reaches Earth from the sun, while others hold heat energy emitted from the Earth's surface.
[vii] Global patterns of atmospheric movement influence local weather. Oceans have a major effect on climate, because water in the oceans hold a large amount of heat.
|
1.1 - Characteristics living things
In ancient times, people believed in spontaneous generation, that is, they believed that life could be generated from nonliving matter. In 1668, Francesco Redi disproved this theory. Back in the day, people believed that rooten meat could turn into maggots because the maggots often appeared in decaying meat. Redi did the experiment shown below,
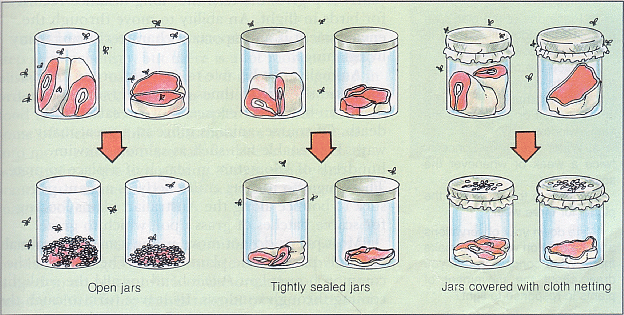
The conclusion from Redi's experiment was that maggots appeared on the meat only if flies were able to enter the jars and lay eggs.
What are living things made of? It took quite a while to figure this out because the basic unit of life, the cell, is too small to be viewed with the naked eye. Only under a microscope can cells be seen. For example, if we were to take a close up of a goat or a leaf we would see the cells that the organism is made of,

This newly found knowledge was the source of the cell theory,
To get an idea of what a cell looks like, here is a picture of a plant cell,
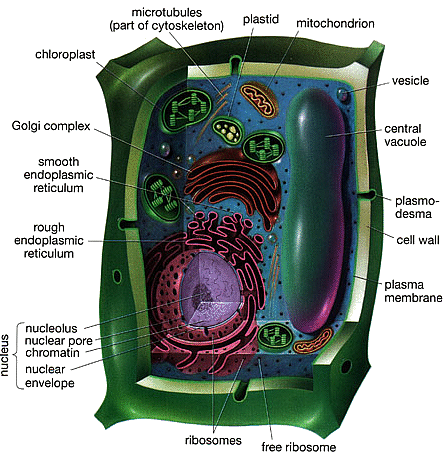
The structure looks very complex. That is why we often use diagrams to illustrate the main ideas. In the case of a cell, we can think of it as a factory with different tasks being performed at different locations within the factory,
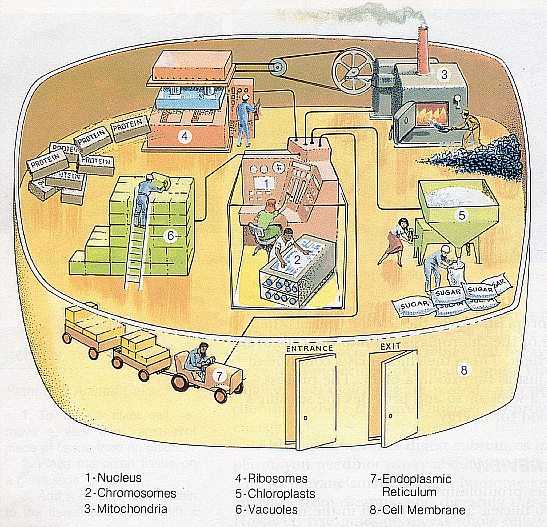
|
2.1 - Matter
...
|
3.1 - The changing earth
...
|
4.1 - Skeletal and Muscular System
...
[1] A Beka SCIENCE 5, OBSERVING GOD'S WORLD, Pensacola, Florida.
...