dba
HARLEM INTERNATIONAL COMMUNITY SCHOOL
Founded 1976, Wallie Simpson, Founder and Principal
7TH Grade Mathematics [Arithmetic 7] |
|
|--Percent and Decimals
|--Percents Greater 100 or Less Than 1
|--Percent Increase or Decrease
|--Simple Interest
|--Adding and Substracting Rational Numbers
|--Equations with Addition and Subtraction
|--Multiplication and Division
|--Rational Numbers and Repeating Decimals
|--Solving Equations Using Square Roots
|--The Pythagorean Theorem
|--Special Triangles
|--Area of Selected Polygons
|--Area of Circles
|--Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
|--Volume of Pyramids and Cones
|--Surface Area
|--Using Letters to Represent Variables
|--Translating Verbal Sentences into Formulas
|--Using Formulas for Perimeter, Area, and Volume
Required Textbook: A Beka Basic Mathematics, Work-Text, Pensacola, Florida, current edition.
[a] Become familiar with basic number theory and study of computations with integers, ordering, graphing, and absolute values.
[i] Write expressions from phrases and word problems, simplify expressions using the associative and distributive properties, and solve expressions for given values of variables.
[ii] Solve one, two, and multi-step equations using inverse operations, order of operations, and properties of addition and multiplication, complete function charts and graph equations and use equations to solve word problems.
[iii] Learn how to solve single and multi-step inequalities, simple and compound inequalities, and use inequalities in word problems and real-life situations.
[iii] Make use of mental math strategies, real number properties, adding decimals, subtracting decimals, multiplying decimals, dividing decimals, solving equations, and writing equations from word problems.
[vi] Learn the basics of statistics, ratios, proportions, and probability.
[v] Order fractions, decimals, and percents and solving practical problems that involve percents.
[b] Measurement units, measurement and geometry.
[i] Learn how to classify geometric shapes, similarity, congruence, and the application of formulas.
[ii] Apply what you have learned in solving real-life problems to demonstrate understanding of the concepts.
[iii] Use exponents and scientific notation to find area and volume.
[iv] Use fractions and mixed numbers in measurements, such as distance and area.
[c] Solve mathematical problems using a variety of methods.
[i] Use integers to solve problems involving signed numbers.
[ii] Use rational numbers to solve problems involving signed numbers.
[iii] Use rational numbers to solve fractional, decimal, percent, and ratio/proportion problems.
[iv] Use four arithmetic operations with integers and rational numbers to solve problems involving signed numbers.
[v] Use square roots to solve problems involving right triangles and squares.
[vi] Identify two dimensional figures to calculate perimeter and area.
[d] Communicate mathematical information using a variety of methods.
[i] Use integers to create number lines.
[ii] Use rational numbers to create number lines.
[iii] Demonstrate the rules for the arithmetic operations for integers and rational numbers.
[iv] Plot points on a number line to represent signed numbers.
[v] Plot points on a Cartesian plane to visually represent ordered pairs.
[vi] Create charts and tables to logically organize and interpret sets of data.
[vii] Identify points, lines, and planes to discuss, draw, and measure Geometric shapes.
|
1.1 - Percent and Decimals
...
|
2.1 - Adding and Substracting Rational Numbers
...
|
3.1 - Solving Equations Using Square Roots
...
|
4.1 - Area of Selected Polygons
...
4.3 - Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
Let us consider how we can measure the volume of a rectangular prism or box. If we measure the distance from one side to
the other we are measuring one dimension, which we can call length (l) or width (w). If we measure both the length
and the width and multiply length times width, we have measured the area of the box's base. Area is
then a two-dimensional measurement.
If we measure the height of the prism and multiply length times width times height, we have computed
the volume of the tree-dimensional object called a rectangular prism or box.
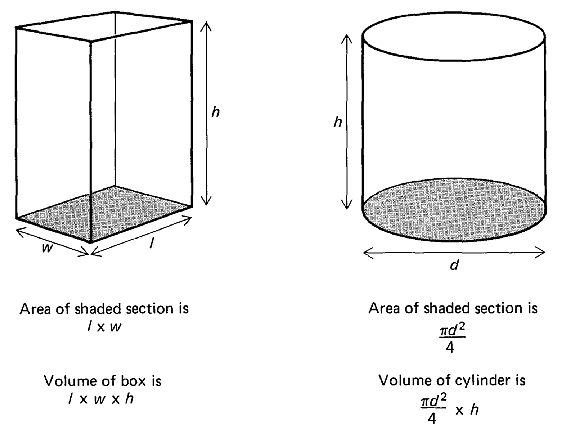
A rectangular prism (box) and a cylinder
The volume of a cylinder is obtained by first computing the area of the base. The base of a cylinder is a circle.
The area of a circle is obtained with the formula,
Area = πR2
Because the radius (R) is equal to half the diameter (d), you can also use the formula,
Area = πd2
---
4
If we measure the height of the cylinder and multiply area times height, we have computed the volume of the tree-dimensional object.
|
5.1 - Using Letters to Represent Variables
...
[1] A Beka Basic Mathematics, Work-Text, Pensacola, Florida.